The objective of the European project BugWright2 is to develop and demonstrate an adaptable autonomous robotic solution for servicing ship outer hulls. By combining the capabilities of autonomous micro air vehicles and small autonomous underwater vehicles, with teams of magnetic-wheeled crawlers operating directly on the surface of the structure, the inspection and cleaning system will be able to seamlessly merge the acquisition of a global overview of the structure with…
Category: Prototypes
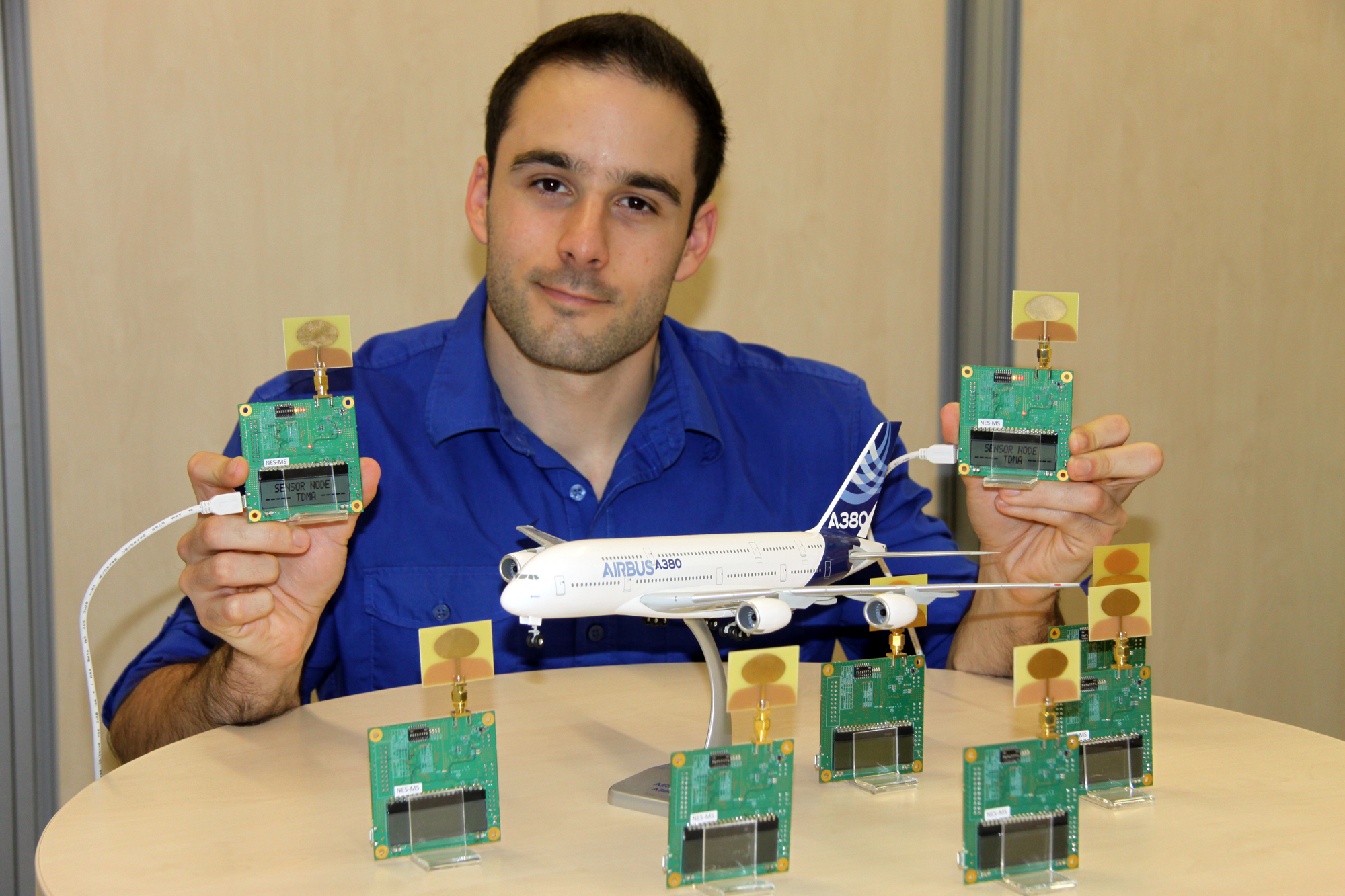
UWB sensor networks in airplanes
Modern airplanes are equipped with hundreds of embedded sensors and actuators necessary for structural health monitoring, aircraft control, and passenger and crew assistance. These devices are typically interconnected by wires. Using wireless connections instead of wires improves flexibility of installations and reduces the airplane’s weight. Researchers from Airbus Group Innovations have been working on this topic for several years. An ongoing joint project with the University of Klagenfurt and Lakeside…
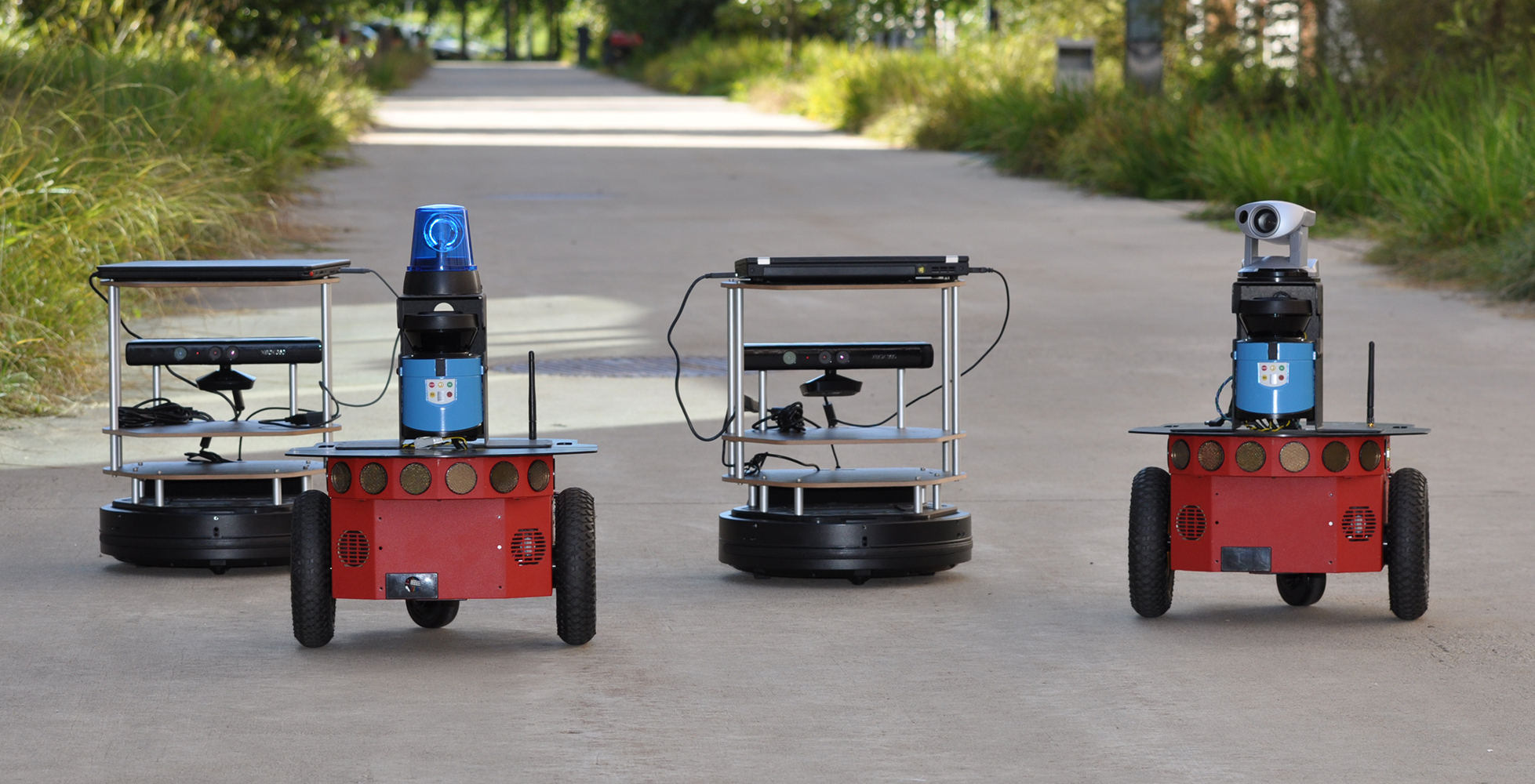
Collaborative mapping with mobile robot teams
New packages for the Robot Operating System (ROS) are available for autonomous exploration of unknown environments using collaborating mobile robots equipped with cameras. The software offers wireless ad hoc communications between robots, merging of maps from different robots, and coordinated selection of exploration frontiers. A prototype with up to four robots was built that demonstrates its functionality in an indoor environment. There is a broad spectrum of applications for mobile…
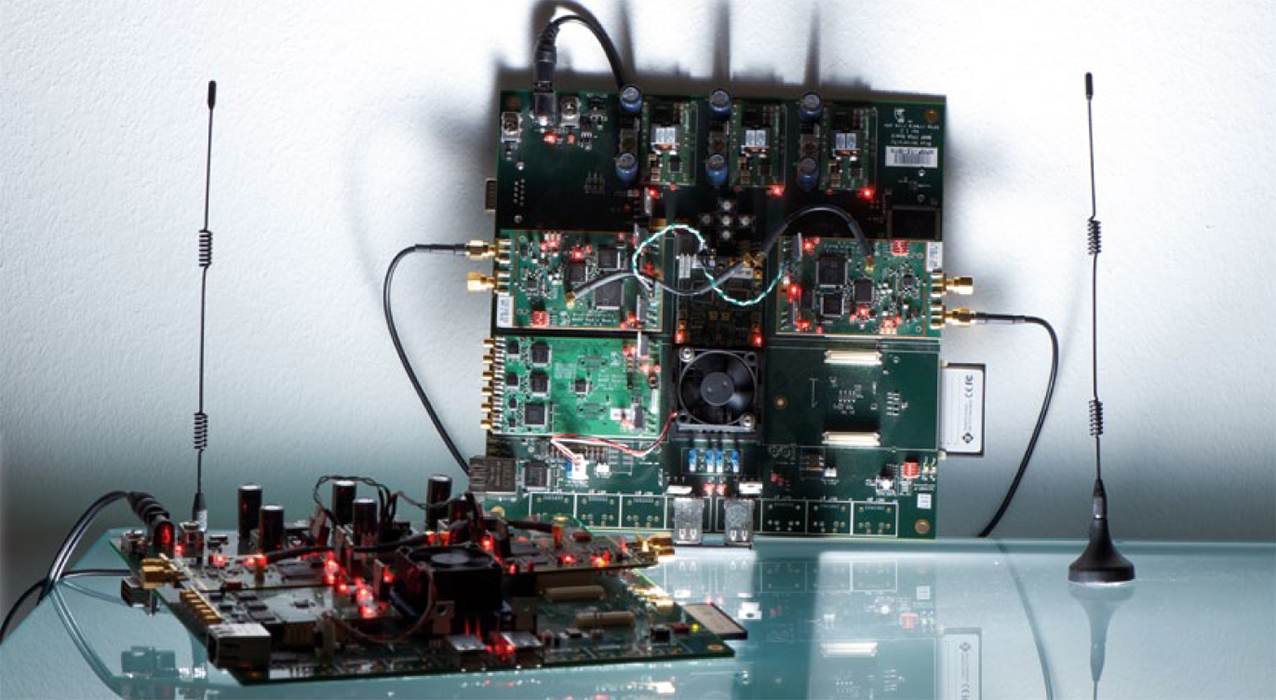
Pulse-coupled oscillator synchronization on FPGA radios
The mathematical modeling of pulse-coupled biological oscillators offers a fully decentralized and scalable approach for time synchronization. There is a broad spectrum of work on pulse-coupled oscillators in physics, biology, neuroscience, and other disciplines. The communications engineering community has been interested to transfer these results to the synchronization of nodes in wireless networks. A one-to-one transfer is infeasible due to the differences between wireless and biological communications. Several extensions and…